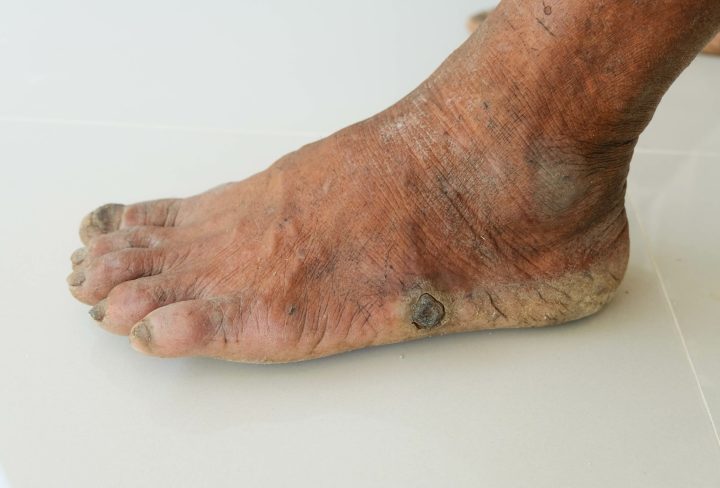
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Among its many complications, diabetic foot problems stand out as a significant concern. High blood sugar levels over time can cause nerve damage (neuropathy) and reduced blood flow to the feet, leading to a range of foot-related complications.
These issues can become serious if not detected and addressed promptly. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with diabetes and their caregivers to be vigilant and recognize the signs of diabetic foot early on.
In this article, we will explore the most common signs of diabetic foot and the importance of seeking medical attention when they arise.
1. NUMBNESS AND TINGLING
One of the primary indicators of diabetic foot problems is neuropathy, which results from nerve damage due to prolonged high blood sugar levels. This condition can cause a loss of sensation in the feet, leading to numbness and tingling sensations. Patients may find it challenging to detect injuries or irritations on their feet due to the reduced ability to feel pain. As a result, even minor wounds can go unnoticed, increasing the risk of infection and other complications.
2. FOOT ULCERS
Foot ulcers are open sores that develop on the skin, often occurring on the bottom of the feet or the sides. These ulcers are common in people with diabetes, particularly those with neuropathy. The combination of reduced sensation and decreased blood flow to the feet can lead to the formation of ulcers from minor injuries, pressure, or friction. If left untreated, these ulcers can become infected and lead to severe complications, such as gangrene.
3. SWELLING AND REDNESS
Another sign of diabetic foot issues is swelling and redness in the feet and ankles. Reduced blood flow can cause fluid to accumulate in the lower extremities, leading to swelling. Additionally, inflammation may occur in response to infections, which are more likely to go unnoticed due to neuropathy. Swelling and redness should never be ignored, as they may indicate an underlying problem that requires immediate attention.
4. PERSISTENT PAIN
While neuropathy can cause a lack of sensation in the feet, it can also lead to paradoxical symptoms like persistent pain. Some individuals with diabetic foot problems experience burning, cramping, or sharp pains, despite the numbness. Persistent pain may be a sign of nerve damage or an underlying infection, and seeking medical evaluation is essential to identify the cause and prevent further complications.
5. CHANGES IN SKIN AND NAIL HEALTH
Observing changes in the skin and nails can also help identify potential diabetic foot issues. Skin that becomes dry, cracked, or peeling may indicate reduced blood flow or neuropathy. Discoloration of the skin, especially darkening, may be a sign of inadequate circulation. Furthermore, changes in the shape and texture of the toenails, such as thickening, yellowing, or ingrown nails, can be related to diabetes and warrant attention.
6. POOR WOUND HEALING
Diabetes can impair the body’s natural healing processes, making it difficult for wounds to heal properly. Even minor cuts, blisters, or abrasions may take an unusually long time to heal or may not heal at all. Poor wound healing can increase the risk of infection and the development of foot ulcers, underscoring the importance of immediate medical attention for any foot injury.
7. FOOT DEFORMITIES
Over time, untreated diabetic foot problems can lead to foot deformities, such as Charcot foot. Charcot foot is a severe condition where the bones in the foot weaken and collapse due to nerve damage, leading to abnormal foot shape and instability. Recognizing early signs of deformities and seeking treatment promptly can prevent further deterioration and disability.
In conclusion, diabetic foot problems are serious complications that require careful monitoring and timely intervention. Individuals with diabetes should pay close attention to their feet, check for any of the mentioned signs regularly, and promptly consult a healthcare professional if any abnormalities are detected. Proper foot care, blood sugar management, and regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can significantly reduce the risk of diabetic foot complications and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals living with diabetes. Remember, prevention and early detection are key to avoiding serious consequences associated with diabetic foot problems.